
The Intersection of Metaverse, Artificial Intelligence, and Cybersecurity
The rapid advancement of the Metaverse and its reliance on emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) has opened up a treasure trove of digital possibilities. From immersive virtual worlds to decentralized interactions, the Metaverse is poised to redefine how individuals and businesses interact. However, as with any technological revolution, there lies a flipside—ensuring robust cybersecurity to mitigate vulnerabilities that come with this convergence of technologies.
Let’s explore how this fusion creates opportunities, challenges, and what measures the industry must adopt to bolster safety in the Metaverse ecosystem.
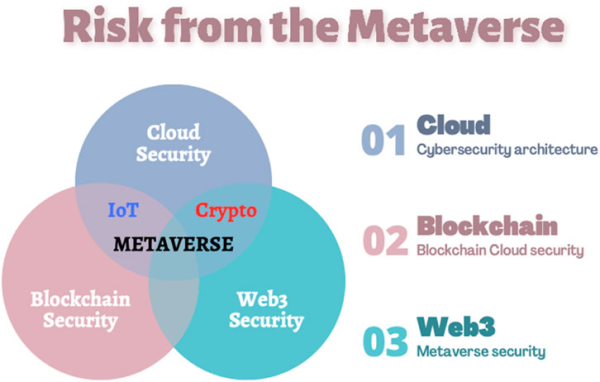
Understanding the Metaverse Ecosystem
The Metaverse is much more than a virtual playground; it’s a complex environment where tangible and digital worlds overlap. Major components of its infrastructure include:
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): These interfaces facilitate immersive interactions.
- Blockchain: Ensures decentralized ownership and security of assets like NFTs within virtual worlds.
- Artificial Intelligence: Enhances personalization, enables autonomous avatars, and provides real-time data analytics.
One of the key trends pushing the development of the Metaverse is its increasing overlap with AI systems. While AI offers immense benefits like personalized experiences and scalability, this dependency on AI also means a new surface for cyberattacks to exploit.
The Cybersecurity Dilemma
As Metaverse platforms become an integral part of workspaces, entertainment, commerce, and social communication, they become lucrative targets for cybercriminals. Threats targeting the Metaverse range from identity theft to data breaches and the manipulation of AI-driven systems. Below are some of the top cyber risks associated with the Metaverse:
- Identity Impersonation and Theft: Avatars in the Metaverse can represent personal or corporate identities, making them vulnerable to impersonation.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Huge amounts of user data—including biometrics and behavioral traits—can be stolen or misused.
- AI Algorithm Exploits: Since AI plays a critical role in Metaverse systems, vulnerabilities in algorithms can be manipulated to disrupt virtual ecosystems.
- Blockchain Vulnerabilities: Although blockchain is secure by design, hackers can exploit smart contract bugs or decentralized exchanges.
Each of these challenges illustrates how the diverse integrations in the Metaverse amplify its attack surface and necessitate a fusion of advanced defensive mechanisms.
The Role of AI in Enhancing Security
While AI creates certain vulnerabilities, it also serves as a powerful tool in combating cyber threats. By leveraging AI-powered systems, the Metaverse can ensure heightened security, relying on features like:
- Real-Time Threat Detection: AI algorithms can identify and mitigate suspicious behaviors, preventing potential fraudulent activities.
- Adaptive Security Frameworks: Machine learning systems can evolve, addressing new types of threats proactively.
- User Identity Authentication: AI adds layers of security through biometric recognition and behavioral analysis.
- Pattern Recognition: AI can track and prevent anomalies in data flow across virtual networks.
This dual role of AI—both as a potential vulnerability and a defense mechanism—underlines the importance of integrating secure frameworks within the AI-powered aspects of the Metaverse.
Blockchain as a Backbone of Metaverse Security
Blockchain technology plays a pivotal role in addressing security challenges within the Metaverse. Its decentralized and immutable infrastructure provides the following benefits:
- Secure Transactions: Blockchain-enabled smart contracts ensure trustless transactions using transparent systems.
- Identity Protection: Decentralized identifiers (DIDs) allow users to control their identity across platforms securely.
- Ownership Verification: Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) can authenticate ownership of virtual assets.
By leveraging blockchain frameworks like Ethereum or Polygon, developers can decentralize sensitive data (reducing hacking risks), strengthening the overall security of Metaverse applications.
Tackling Legal and Ethical Concerns
Amid the technological advancements, the regulatory framework for the Metaverse grows increasingly murky. Legal ambiguities around data privacy, consent, intellectual property, and security liabilities pose challenges for the safe adoption of Metaverse technologies. Clear global standards are needed to address issues such as jurisdiction in case of cybercrimes committed within virtual spaces.
Moreover, ethical considerations are critical in ensuring that AI-driven systems do not perpetuate biases or marginalize users.
Steps Forward: Building a Resilient Metaverse
To create a resilient and secure Metaverse, stakeholders must collaborate across multiple dimensions. Recommendations include:
1. Establishing Cross-Industry Standards
Bringing together technology providers, regulators, and researchers to set global best practices for cybersecurity protocols in Metaverse development.
2. Investing in Security Research
Development funds should prioritize research into securing AI systems, detecting vulnerabilities in AR/VR hardware, and testing blockchain applications for loopholes.
3. User Education
Perhaps the most overlooked aspect of cybersecurity is the human factor. Educating Metaverse users about potential threats and safe practices is essential to reducing risks.
4. Ethical AI Development
Ensuring that cybersecurity solutions are devoid of algorithmic biases and have built-in safety measures will foster user trust in the Metaverse ecosystem.
Conclusion
The convergence of the Metaverse, AI, and Blockchain technologies signals an exciting era of innovation. However, this growth introduces unique cybersecurity challenges that require an equally innovative response. By embracing a proactive approach—grounded in advanced threat detection, ethical AI implementation, and transparent blockchain systems—the Metaverse can become a sustainable and secure digital domain.
As technology continues to push boundaries, securing these interconnected ecosystems will be critical for safeguarding user experiences, digital assets, and trust in the next evolution of the internet. The future of the Metaverse lies in its ability to inspire seamless, safe, and immersive interactions for everyone.

Leave a Reply